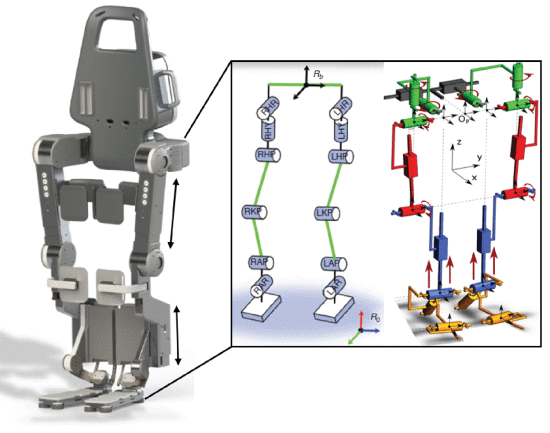
Design of a Turn in Place Controller of an Exoskeleton and Reachability Analysis.
This was a project that was done for the EECS 563: Hybrid Systems: Specification, Verification and Control course taught by Professor Necmiye Ozay.
Summary.
The objective of this project was to create a controller for the turn in place motion of the exoskeleton Atalante designed by Wandercraft, and to analyze the robustness of the controller by calculating the system’s reachable set. Turning in place is an important motion to achieve because it enables the exoskeleton to rapidly change directions allowing the user to perform tasks such as grasping an item, walking in a different direction, or sitting down. Many of the challenges that were encountered while investigating this problem came from the nonlinear and high degree-of-freedom hybrid dynamics.
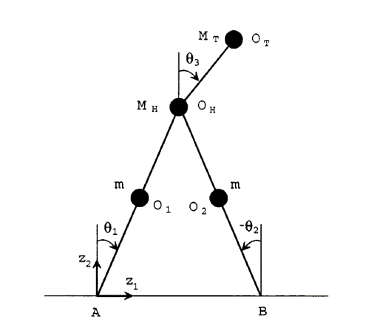
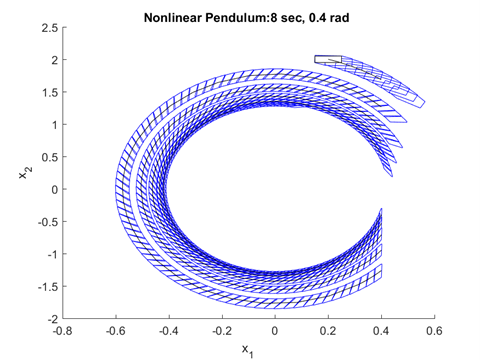
The optimization toolbox Fast Robot Optimization and Simulation Toolkit by Professor Ayonga Hereid was utilized to generate the desired trajectories for turn in place. The reachability analysis was performed using CORA. Calculating the reachable set was a particularly challenging problem as most of the methods used to calculate reachable sets are not scalable. Therefore, the reachability analysis was first performed for a pendulum hitting a wall system and a three link robot walking. Unfortunately, due to time constraints, the reachability analysis of the exoskeleton was left for future work.
For more details please see the sections below.
Atalante turning -360 degrees at -14 degrees per step
Turn in Place Details
Reachability
References
M. E. Mungai and J. W. Grizzle, "Feedback Control Design for Robust Comfortable Sit-to-Stand Motions of 3D Lower-Limb Exoskeletons," in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 122-161, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3046446.
Westervelt E., Grizzle J., Chevallereau C., Choi J., et al. Feedback Control of Dynamic Bipedal Robot Locomotion. CRC Press: 2007.
Kajita S., Kanehiro F., Kaneko K., Yokoi K., et al. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(29Oct-3Nov. 2001). 10.1109/IROS.2001.973365